Google BigQuery Create Structure activity¶
Introduction¶
A Google BigQuery Create Structure activity, using its Google BigQuery connection, creates datasets or tables in Google BigQuery and is intended to be used as a target to consume data in an operation.
Quotas and limits¶
Google BigQuery enforces quotas and limits, which limit the rate and volume of structures being created. When these limits are reached, the operation may complete with a Success operation status even if all requested structures are not created. Check the operation logs for any rate limit errors returned from the Google BigQuery SDK. For more information, see Google's documentation.
Create a Google BigQuery Create Structure activity¶
An instance of a Google BigQuery Create Structure activity is created from a Google BigQuery connection using its Create Structure activity type.
To create an instance of an activity, drag the activity type to the design canvas or copy the activity type and paste it on the design canvas. For details, see Create an activity instance in Component reuse.
An existing Google BigQuery Create Structure activity can be edited from these locations:
- The design canvas (see Component actions menu in Design canvas).
- The project pane's Components tab (see Component actions menu in Project pane Components tab).
Configure a Google BigQuery Create Structure activity¶
Follow these steps to configure a Google BigQuery Create Structure activity:
-
Step 1: Enter a name and select object
Provide a name for the activity and select object. -
Step 2: Select a sub-object
Select a sub-object. -
Step 3: Review the data schemas
Any request or response schemas are displayed.
Step 1: Enter a name and select object¶
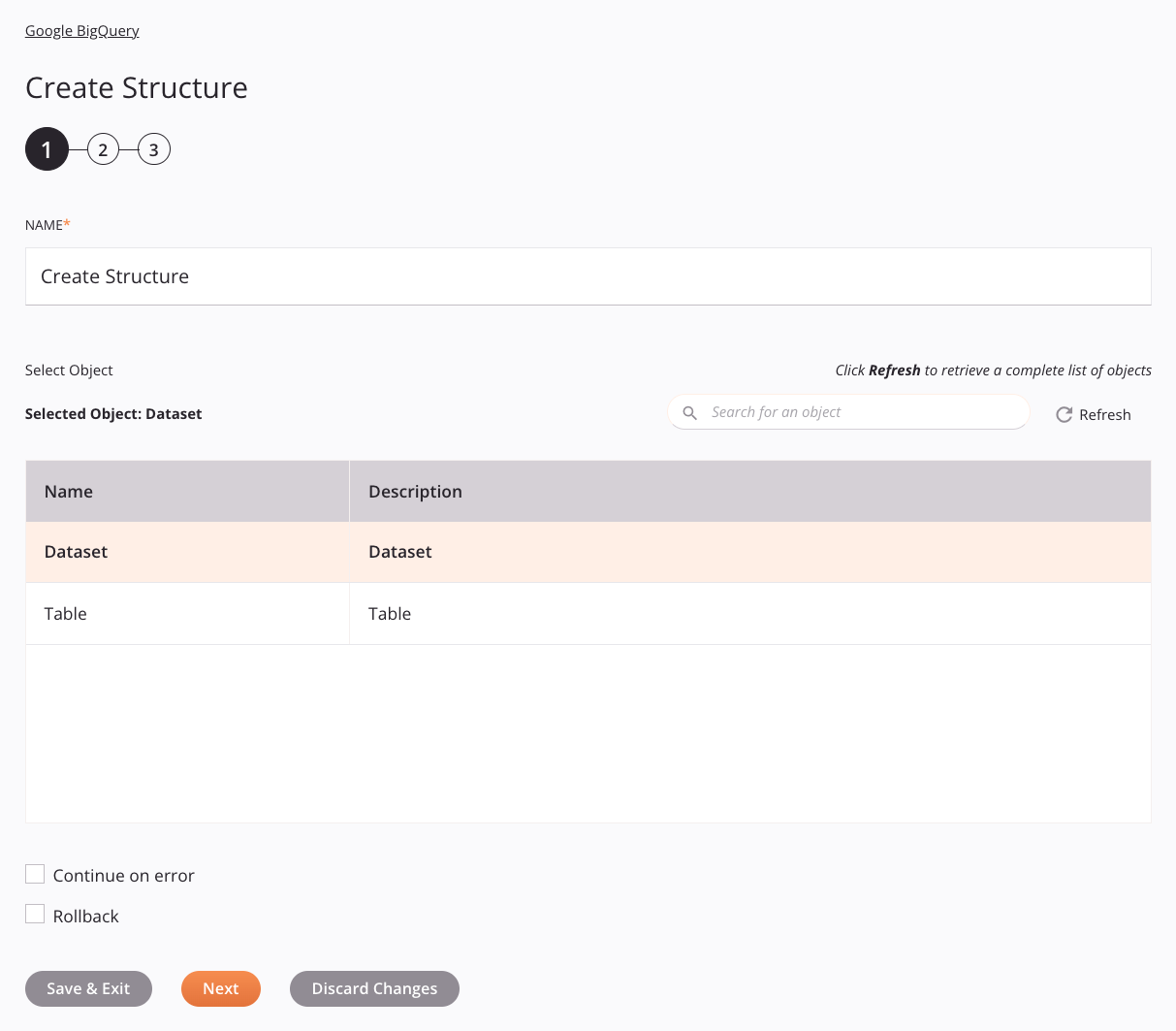
In this step, provide a name for the activity and select object. Each user interface element of this step is described below.
-
Name: Enter a name to identify the activity. The name must be unique for each Google BigQuery Create Structure activity and must not contain forward slashes
/or colons:. -
Select Object: This section displays objects available in the Google BigQuery endpoint.
-
Selected Object: After an object is selected, it is listed here.
-
Search: Enter any column's value into the search box to filter the list of objects. The search is not case-sensitive. If objects are already displayed within the table, the table results are filtered in real time with each keystroke. To reload objects from the endpoint when searching, enter search criteria and then refresh, as described below.
-
Refresh: Click the refresh icon
 or the word Refresh to reload objects from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This may be useful if objects have been added to Google BigQuery. This action refreshes all metadata used to build the table of objects displayed in the configuration.
or the word Refresh to reload objects from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This may be useful if objects have been added to Google BigQuery. This action refreshes all metadata used to build the table of objects displayed in the configuration. -
Selecting an Object: Within the table, click anywhere on a row to select an object. Only one object can be selected. The information available for each object is fetched from the Google BigQuery endpoint:
-
Name: The name of the object.
-
Description: The description of the object.
-
Tip
If the table does not populate with available objects, the Google BigQuery connection may not be successful. Ensure you are connected by reopening the connection and retesting the credentials.
-
-
Continue on Error: Select to continue the activity execution if an error is encountered for a dataset in a batch request. If any errors are encountered, they are written to the operation log.
-
Rollback: If errors occur during structure creation, this option (when selected) reverts any changes made prior to the error. If unselected, any changes prior to the error will persist.
-
Save & Exit: If enabled, click to save the configuration for this step and close the activity configuration.
-
Next: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and continue to the next step. The configuration will not be saved until you click the Finished button on the last step.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes, click to close the configuration without saving changes made to any step. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
Step 2: Select a sub-object¶
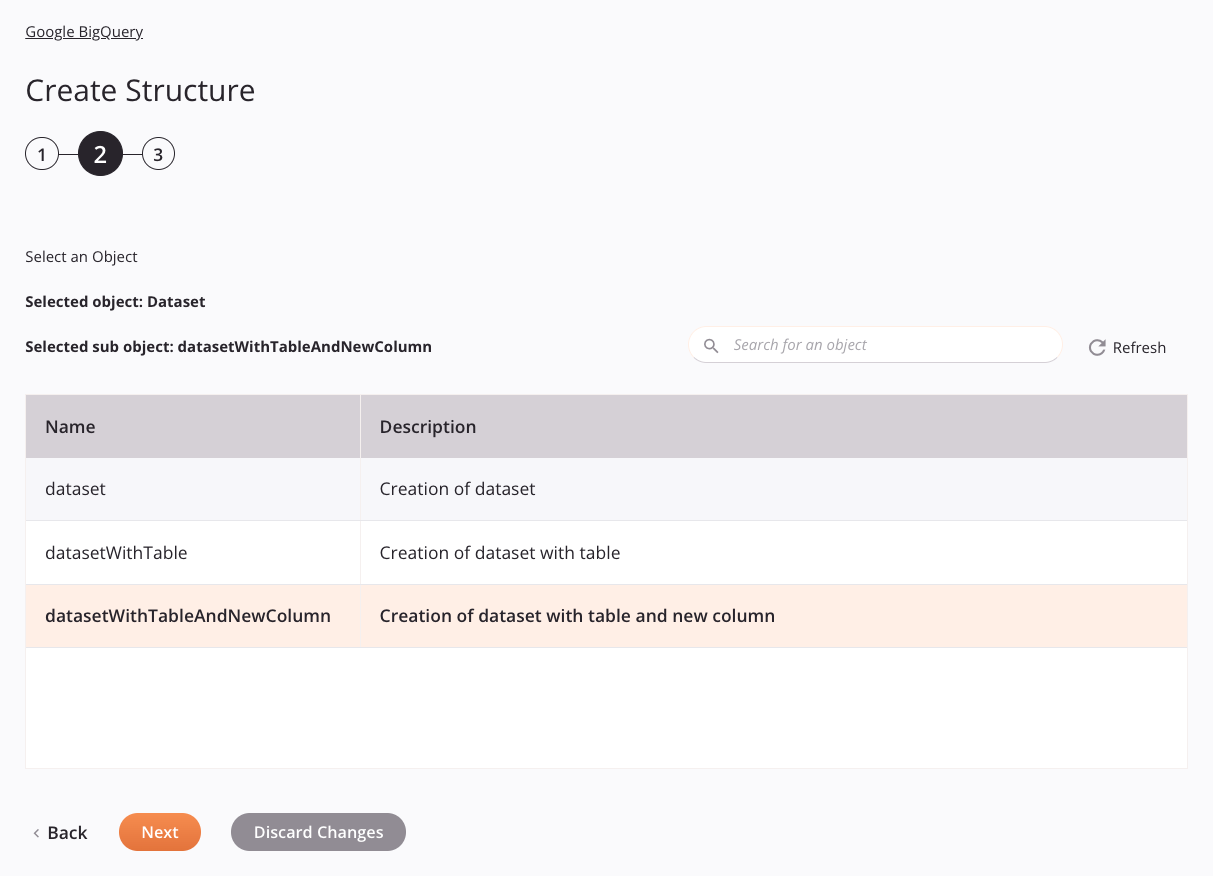
In this step, select a sub-object. Each user interface element of this step is described below.
-
Select a Sub-object: This section displays sub-objects available in the Google BigQuery endpoint.
-
Selected Object: The object selected in the previous step is listed here.
-
Selected Sub-object: After a sub-object is selected, it is listed here.
-
Search: Enter any column's value into the search box to filter the list of sub-objects. The search is not case-sensitive. If sub-objects are already displayed within the table, the table results are filtered in real time with each keystroke. To reload sub-objects from the endpoint when searching, enter search criteria and then refresh, as described below.
-
Refresh: Click the refresh icon
 or the word Refresh to reload sub-objects from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This may be useful if sub-objects have been added to Google BigQuery. This action refreshes all metadata used to build the table of sub-objects displayed in the configuration.
or the word Refresh to reload sub-objects from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This may be useful if sub-objects have been added to Google BigQuery. This action refreshes all metadata used to build the table of sub-objects displayed in the configuration. -
Selecting a Sub-object: Within the table, click anywhere on a row to select a sub-object. Only one sub-object can be selected. The information available for each sub-object is fetched from the Google BigQuery endpoint:
-
Name: The name of the sub-object.
-
Description: The description of the sub-object.
-
Tip
If the table does not populate with available sub-objects, the Google BigQuery connection may not be successful. Ensure you are connected by reopening the connection and retesting the credentials.
-
-
Back: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and return to the previous step.
-
Next: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and continue to the next step. The configuration will not be saved until you click the Finished button on the last step.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes, click to close the configuration without saving changes made to any step. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
Step 3: Review the data schemas¶
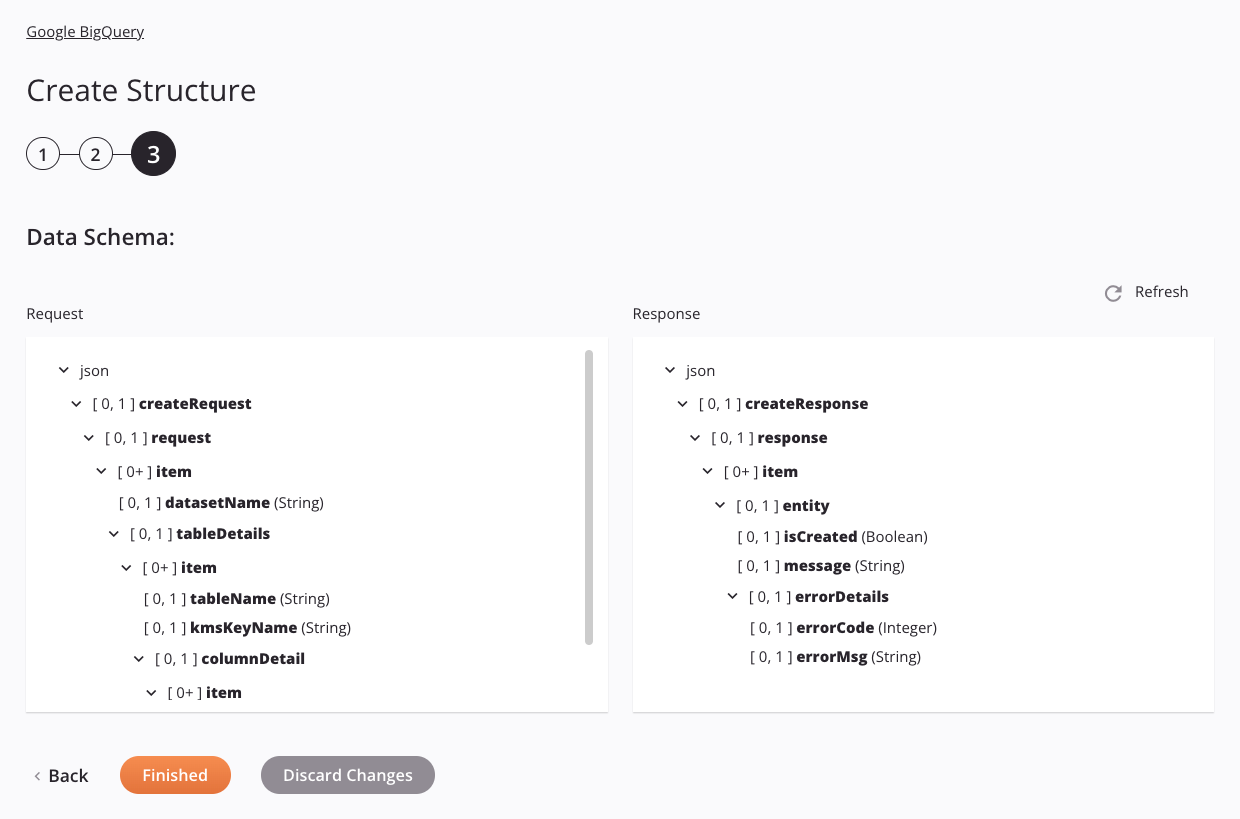
Any request or response schemas are displayed. Each user interface element of this step is described below.
-
Data Schemas: These data schemas are inherited by adjacent transformations and are displayed again during transformation mapping.
The Google BigQuery connector uses the Google SDK version 25.4.0. Refer to the SDK documentation for information on the schema nodes and fields.
Important
Google BigQuery enforces quotas and limits, which limit the rate and volume of structures being created. When these limits are reached, the activity will complete with a
Successoperation status, even if all requested structures are not created. For more information, see Google's documentation.The Create Structure activity uses JSON in both its request and response schemas.
-
Refresh: Click the refresh icon
 or the word Refresh to regenerate schemas from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This action also regenerates a schema in other locations throughout the project where the same schema is referenced, such as in an adjacent transformation.
or the word Refresh to regenerate schemas from the Google BigQuery endpoint. This action also regenerates a schema in other locations throughout the project where the same schema is referenced, such as in an adjacent transformation. -
Back: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and return to the previous step.
-
Finished: Click to save the configuration for all steps and close the activity configuration.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes, click to close the configuration without saving changes made to any step. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
Next steps¶
After configuring a Google BigQuery Create Structure activity, complete the configuration of the operation by adding and configuring other activities, transformations, or scripts as operation steps. You can also configure the operation settings, which include the ability to chain operations together that are in the same or different workflows.
Menu actions for an activity are accessible from the project pane and the design canvas. For details, see Activity actions menu in Connector basics.
Google BigQuery Create Structure activities can be used as a target with these operation patterns:
- Transformation pattern
- Two-transformation pattern (as the first or second target)
To use the activity with scripting functions, write the data to a temporary location and then use that temporary location in the scripting function.
When ready, deploy and run the operation and validate behavior by checking the operation logs.