RabbitMQ connection¶
Introduction¶
A RabbitMQ connection, created using the RabbitMQ connector, establishes access to RabbitMQ. Once a connection is configured, you can create instances of RabbitMQ activities associated with that connection to be used either as sources (to provide data in an operation) or as targets (to consume data in an operation).
The RabbitMQ connector supports Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP), a protocol for business messaging. Using AMQP requires a secure connection and CA-certified certificates.
Note
This connector supports the Enable Re-authentication on Change organization policy. If enabled, a change to the Hostname, Username, or Virtual Host in this connection requires users to re-enter the Password for the connection.
Create or edit a RabbitMQ connection¶
A new RabbitMQ connection is created using the RabbitMQ connector from one of these locations:
- The design component palette's Project endpoints and connectors tab (see Design component palette).
- The Global Connections page (see Create a global connection in Global Connections).
An existing RabbitMQ connection can be edited from these locations:
- The design component palette's Project endpoints and connectors tab (see Design component palette).
- The project pane's Components tab (see Component actions menu in Project pane Components tab).
- The Global Connections page (see Edit a global connection in Global Connections).
Configure a RabbitMQ connection¶
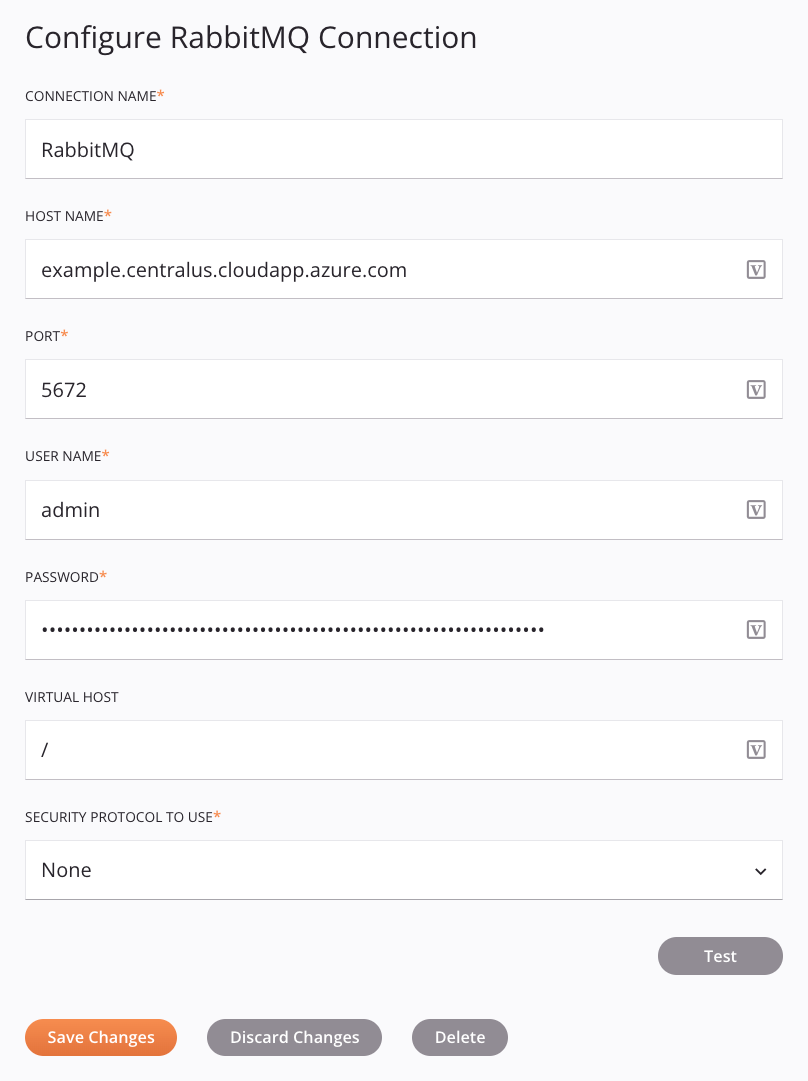
Each user interface element of the RabbitMQ connection configuration screen is described below.
Tip
Fields with a variable icon ![]() support using global variables, project variables, and Jitterbit variables. Begin either by typing an open square bracket
support using global variables, project variables, and Jitterbit variables. Begin either by typing an open square bracket [ into the field or by clicking the variable icon to display a list of the existing variables to choose from.
-
Connection Name: Enter a name to use to identify the connection. The name must be unique for each RabbitMQ connection and must not contain forward slashes
/or colons:. This name is also used to identify the RabbitMQ endpoint, which refers to both a specific connection and its activities. -
Host Name: Enter the host for the instance.
-
Port: Enter the port for the instance. The default ports for RabbitMQ instances are ports
5672for regular connections; and5671for connections that use TLS. -
Username: Enter the username for the instance.
-
Password: Enter the password for the instance.
-
Virtual Host: Enter the virtual host.
-
Security Protocol to use: Select the security protocol to use, either None, TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2, TLSv1.3. For more information, see RabbitMQ's TLS documentation.
-
Test: Click to verify the connection using the provided configuration. When the connection is tested, the latest version of the connector is downloaded by the agent(s) in the agent group associated with the current environment. This connector supports suspending the download of the latest connector version by using the Disable Auto Connector Update organization policy.
-
Save Changes: Click to save and close the connection configuration.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes to a new or existing configuration, click to close the configuration without saving. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
-
Delete: After opening an existing connection configuration, click to permanently delete the connection from the project and close the configuration (see Component dependencies, deletion, and removal). A message asks you to confirm that you want to delete the connection.
Next steps¶
After a RabbitMQ connection has been created, you place an activity type on the design canvas to create activity instances to be used either as sources (to provide data in an operation) or as targets (to consume data in an operation).
Menu actions for a connection and its activity types are accessible from the project pane and design component palette. For details, see Actions menus in Connector basics.
These activity types are available:
-
Publish Bulk: Publishes a batch of messages to an exchange in RabbitMQ and is intended to be used as a target in an operation.
-
Get Bulk: Retrieves a batch of messages available in a specific RabbitMQ queue and is intended to be used as a source in an operation.
-
Acknowledge: Acknowledges a message (using an
ackId) in RabbitMQ and is intended to be used as a target in an operation. -
Get: Retrieves messages from a RabbitMQ queue and is intended to be used as a source in an operation.
-
Publish: Publishes a message to an exchange in RabbitMQ and is intended to be used as a target in an operation.
-
Consume: Consumes messages from a RabbitMQ queue and is intended to be used as a source in an operation.