Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity
Introduction
A Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity, using its Jitterbit MQ connection, sends a batch of messages to a Jitterbit message queue and is intended to be used as a target to consume data in an operation.
Note
The Send Bulk activity sends a batch of messages to a Jitterbit message queue. To send a single message to a Jitterbit message queue, use the Send activity.
Create a Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity
An instance of a Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity is created from a Jitterbit MQ connection using its Send Bulk activity type.
To create an instance of an activity, drag the activity type to the design canvas or copy the activity type and paste it on the design canvas. For details, see Create an activity instance in Component reuse.
An existing Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity can be edited from these locations:
- The design canvas (see Component actions menu in Design canvas).
- The project pane's Components tab (see Component actions menu in Project pane Components tab).
Configure a Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity
Follow these steps to configure a Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity:
-
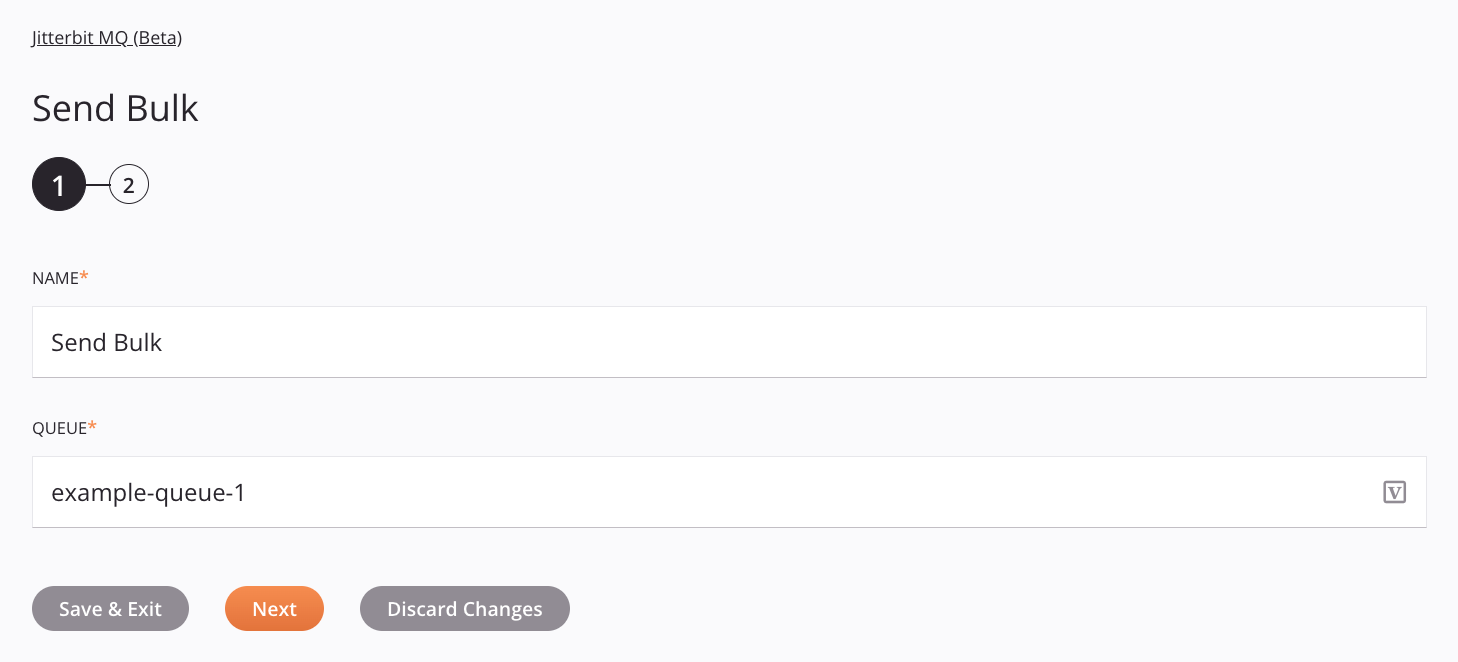
Step 1: Enter a name and queue
Provide a name for the activity and specify the queue. -
Step 2: Review the data schemas
Any request or response schemas are displayed.
Step 1: Enter a name and queue
In this step, provide a name for the activity and specify the queue. Each user interface element of this step is described below.
Tip
Fields with a variable icon ![]() support using global variables, project variables, and Jitterbit variables. Begin either by typing an open square bracket
support using global variables, project variables, and Jitterbit variables. Begin either by typing an open square bracket [ into the field or by clicking the variable icon to display a list of the existing variables to choose from.
-
Name: Enter a name to identify the activity. The name must be unique for each Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity and must not contain forward slashes
/or colons:. -
Queue: Provide the name of the queue to send messages to. The queue must be in the environment specified in the Jitterbit MQ connection.
-
Save & Exit: If enabled, click to save the configuration for this step and close the activity configuration.
-
Next: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and continue to the next step. The configuration will not be saved until you click the Finished button on the last step.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes, click to close the configuration without saving changes made to any step. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
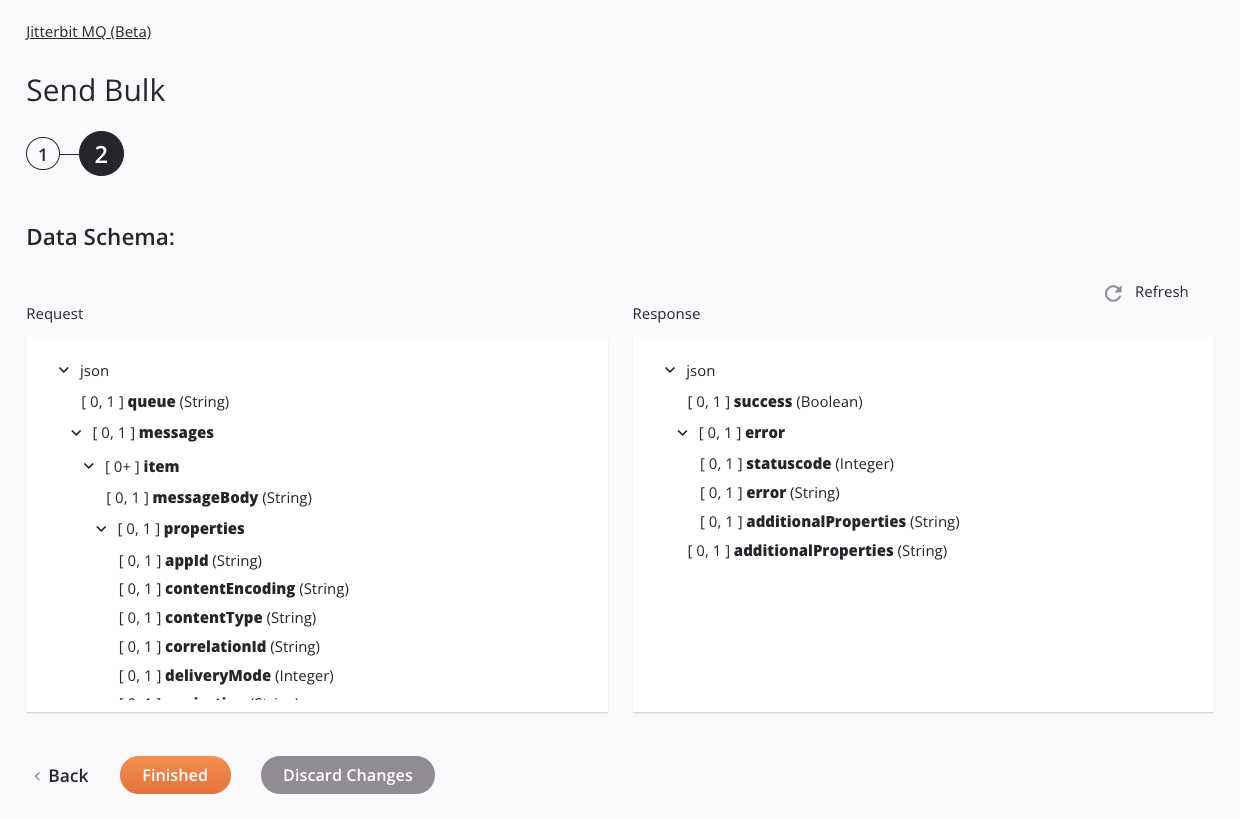
Step 2: Review the data schemas
Any request or response schemas are displayed. Each user interface element of this step is described below.
-
Data Schemas: These data schemas are inherited by adjacent transformations and are displayed again during transformation mapping.
Note
Data supplied in a transformation takes precedence over the activity configuration.
The request data schemas consist of these nodes and fields:
Request Schema Node/Field Description queueThe name of the queue to send messages to; the queue must be in the environment specified in the Jitterbit MQ connection messagesNode containing the messages to be sent to the queue itemNode containing each message to be sent to the queue messageBodyThe message body propertiesNode containing the properties of the message appIdThe identifier of the application that produced the message contentEncodingContent encoding for the message contentTypeThe message content type, such a application/jsoncorrelationIdThe ID of the correlated message (which request the message is replying to) deliveryModeInteger indicating whether the retrieved message is persisted to disk ( 2) or non-persistent (1)expirationThe expiration time after which the message will be deleted (the TTL period in milliseconds as determined in the message queue settings) messageIdThe message ID (if applications need to identify messages, it is recommended that they use this attribute instead of putting it into the message payload); a maximum of 255 characters is allowed priorityInteger value ranging from 0through9indicating the priority of the message (9being the lowest priority)typeString containing the message type, for example, the type of event or command this message represents timestampThe time of the request headersNode containing any message headers itemNode containing each message header nameThe name of the message header valueThe value of the message header Response Schema Node/Field Description successBoolean representing the success ( true) or failure (false) of the acknowledgementerrorNode containing any errors statusCodeHTTP response status code returned errorString containing any error messages additionalPropertiesString containing any additional properties additionalPropertiesString containing any additional properties -
Refresh: Click the refresh icon
 or the word Refresh to regenerate schemas from the Jitterbit MQ endpoint. This action also regenerates a schema in other locations throughout the project where the same schema is referenced, such as in an adjacent transformation.
or the word Refresh to regenerate schemas from the Jitterbit MQ endpoint. This action also regenerates a schema in other locations throughout the project where the same schema is referenced, such as in an adjacent transformation. -
Back: Click to temporarily store the configuration for this step and return to the previous step.
-
Finished: Click to save the configuration for all steps and close the activity configuration.
-
Discard Changes: After making changes, click to close the configuration without saving changes made to any step. A message asks you to confirm that you want to discard changes.
Next steps
After configuring a Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activity, complete the configuration of the operation by adding and configuring other activities, transformations, or scripts as operation steps. You can also configure the operation settings, which include the ability to chain operations together that are in the same or different workflows.
Menu actions for an activity are accessible from the project pane and the design canvas. For details, see Activity actions menu in Connector basics.
Jitterbit MQ Send Bulk activities can be used as a target with these operation patterns:
- Transformation pattern
- Two-transformation pattern (as the first or second target)
To use the activity with scripting functions, write the data to a temporary location and then use that temporary location in the scripting function.
When ready, deploy and run the operation and validate behavior by checking the operation logs.